It seems I was put on the planet to educate people about the negative economic impact of excessive government. I must be doing a bad job, because the burden of the public sector keeps rising.
But hope springs eternal. To help make the case, I’ve cited research from international bureaucracies such as the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, International Monetary Fund, World Bank, and European Central Bank. Since most of those organizations lean to the left, these results should be particularly persuasive.
I’ve also cited the work of academic scholars from all over the world, including the United States, Australia, and Sweden. The evidence is very persuasive that big government is associated with weaker economic performance.
Now we have some new research from the United Kingdom. The Centre for Policy Studies has released a new study, authored by Ryan Bourne and Thomas Oechsle, examining the relationship between economic growth and the size of the public sector.
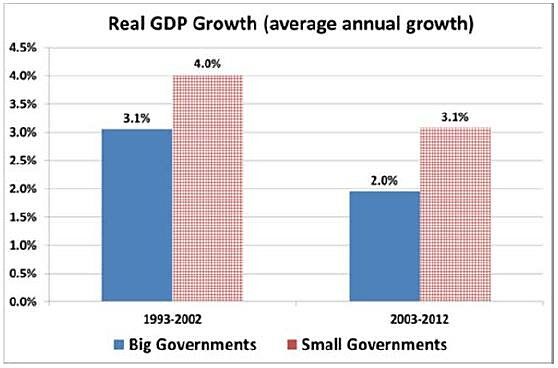
The chart above compares growth rates for nations with big governments and small governments over the past two decades. The difference is significant, but that’s just the tip of the iceberg. The most important findings of the report are the estimates showing how more spending and more taxes are associated with weaker performance.
Here are some key passages from the study.
Using tax to GDP and spending to GDP ratios as a proxy for size of government, regression analysis can be used to estimate the effect of government size on GDP growth in a set of countries defined as advanced by the IMF between 1965 and 2010. …As supply-side economists would expect, the coefficients on the tax revenue to GDP and government spending to GDP ratios are negative and statistically significant. This suggests that, ceteris paribus, a larger tax burden results in a slower annual growth of real GDP per capita. Though it is unlikely that this effect would be linear (we might expect the effect to be larger for countries with huge tax burdens), the regressions suggest that an increase in the tax revenue to GDP ratio by 10 percentage points will, if the other variables do not change, lead to a decrease in the rate of economic growth per capita by 1.2 percentage points. The result is very similar for government outlays to GDP, where an increase by 10 percentage points is associated with a fall in the economic growth rate of 1.1 percentage points. This is in line with other findings in the academic literature. …The two small government economies with the lowest marginal tax rates, Singapore and Hong Kong, were also those which experienced the fastest average real GDP growth.
The folks at CPS also put together a short video to describe the results. It’s very well done, though I’m not a big fan of the argument near then end that faster growth is a good thing because it generates more tax revenue to finance more government. Since I’m a big proponent of the Laffer Curve, I don’t disagree with the premise, but I would argue that additional revenues should be used to finance lower tax rates.
Since I’m nit-picking, I’ll also say that the study should have emphasized that government spending is bad for growth because it inevitably and necessarily leads to the inefficient allocation of resources, and that would be true even if revenues magically floated down from heaven and there was no need for punitive tax rates.
This is my message in this video on the Rahn Curve.
When the issue is government, size matters, and bigger is not better.