In response to President Donald Trump’s call for a border wall, some members of Congress have instead offered a “virtual wall”—ocean-to-ocean border surveillance with technology, especially unmanned aircraft known as drones. U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) already operates a fleet of nine unmanned aircraft. Although drones have been widely used in foreign battlefields, they have failed to help CBP apprehend illegal border crossers and seize drugs. Drones have led to only 0.5 percent of apprehensions at a cost of $32,000 per arrest.
At the same time, drones undermine Americans’ privacy. Their surveillance records the daily lives of Americans living along the border, and because CBP regularly uses its drones to support the operations of other federal agencies as well as state and local police, its drones allow for government surveillance nationwide with minimal oversight and without warrants. CBP should wind down its drone program and, in the meantime, establish more robust privacy protections.
Background
Since fiscal year 2006, CBP’s Air and Marine Operations has operated Predator B drones, a version of the military’s MQ-9 Reaper drone, along the border.1 A drone crew consisting of a pilot, a sensor operator, and a radar operator controls the aircraft and relays information about suspected crossings to the U.S. Border Patrol.2 In September 2017, CBP began testing smaller hand-launched drones, including AeroVironment’s Raven and Puma small unmanned aircraft systems.3 In the summer of 2016, the agency solicited offers for small drones with facial recognition capability.4 The agency will finish its review of the hand-launched systems in spring 2018.5
Limitations of Drones
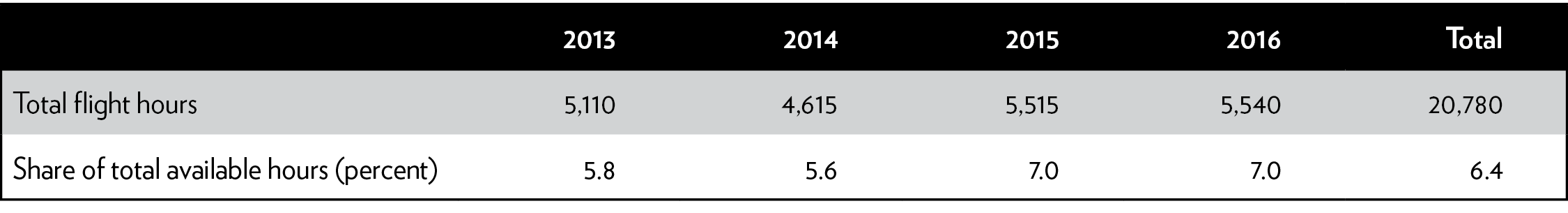
The biggest difficulty with drones is positioning them to surveil the border. Although CBP often comes close to or exceeds its flight-hour goals, its Predators were airborne only 6.4 percent of available hours per year from 2013 to 2016 (Table 1)—on average just 1 hour and 35 minutes per day.6 CBP’s other aerial assets, such as unmanned buoyant aircraft outfitted with Tethered Aerostat Radar System (TARS), conduct surveillance at 15,000 feet and operate around 60 percent of the time.7 A Predator B drone engine cannot regularly handle its maximum flight of 20 hours; even 6 or 7 hours of operation per day would cut at least 15 years off the 20-year lifespans of such engines.8
Table 1: Total flight hours for CBP Predator B drones and share of total available hours, 2013–2016
Source: Government Accountability Office.
CBP managed to conduct only 69 percent of its scheduled drone launches in 2016.9 The agency canceled 20 percent of its drone flights because of weather alone. When the flights do take place, weather can prevent drones from flying in the highest value airspace.10 Even occasional cloud cover can disrupt surveillance. In 2010, CBP allowed CNN to record an incident where operators tracked a group across the border, but just as the pilots started to instruct the agents on the ground, clouds blocked their view, and the subjects escaped.11 Unlike U.S. Border Patrol agents in the field, drones cannot apprehend subjects.
Moreover, two of the CBP drones (18 percent of its fleet) have crashed within just 10 years of purchase—one because of human error in 2006 and another owing to a generator failure in 2014.12 The U.S. Air Force has crashed the same share of its version of the Predator B.13 Of the 15 CBP or military crashes where the cause is publicly known, seven occurred because of mechanical failure, five were caused by pilot error, two by a combination of mechanical and pilot failure, and one by the weather.14
CBP drones also lack the authority to fly in certain areas. They require advanced permission from the U.S. Department of Defense to fly in restricted airspace and they cannot fly in areas with a high volume of commercial flights.15 Such restrictions block off large areas near San Diego, California, and Yuma, Arizona. Drones regularly patrolled only about 170 miles of the 2,000-mile southern land border in 2013, according to the most recent available data.16 For these reasons, CBP drones fail to replace or displace any other surveillance equipment or agents in the field.
Effectiveness Of Drones
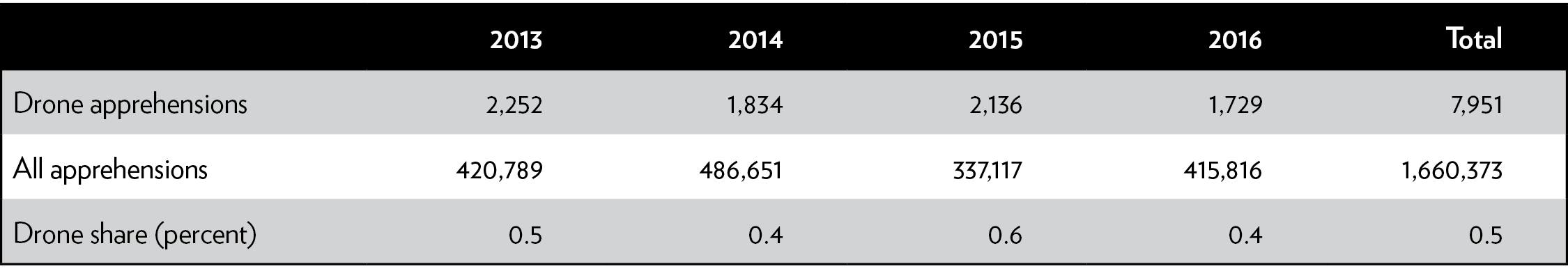
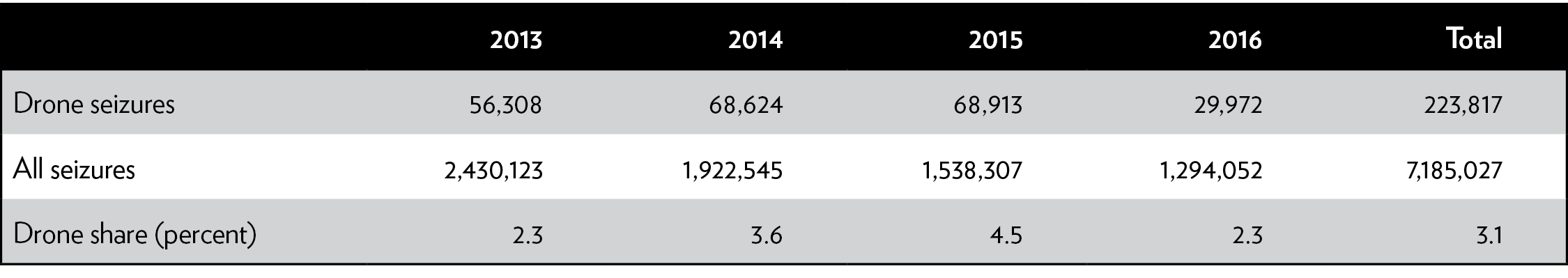
When CBP drones do fly, they contribute little to border security. From 2013 to 2016, the U.S. Border Patrol attributed fewer than 8,000 of its 1.7 million apprehensions to drones (Table 2).17 During the same years, only 3 percent of all U.S. Border Patrol marijuana seizures—which account for 99.3 percent of Border Patrol’s drug seizures by weight—occurred in part because of drones (Table 3).18 The agency has not provided any estimate of how many of these seizures or apprehensions would have occurred anyway had drones not identified them.
Table 2: Apprehensions attributable to drones and all apprehensions, 2013—2016
Sources: United States Border Patrol; Government Accountability Office.
Table 3: Marijuana seizures attributable to drones and all seizures, 2013—2016
Sources: United States Border Patrol; Government Accountability Office.
CBP asserts that drones detect patterns of illegal entries, allowing the agency to reposition its assets accordingly. However, only 2 percent of drone missions resulted in any evidence of a previously undetected illegal crossing in 2014.19 Moreover, the Government Accountability Office found that drones detected only 21,384 suspected border crossers from 2014 to 2016.20 Yet during this time, the U.S. Border Patrol apprehended 1.2 million people while an estimated 570,000 evaded capture.21 In other words, drones may have detected at most 1.2 percent of total illegal border crossings.
Cost Of Drones
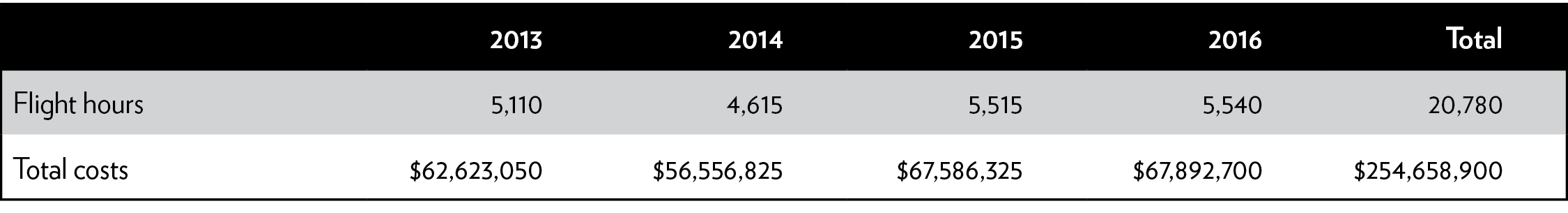
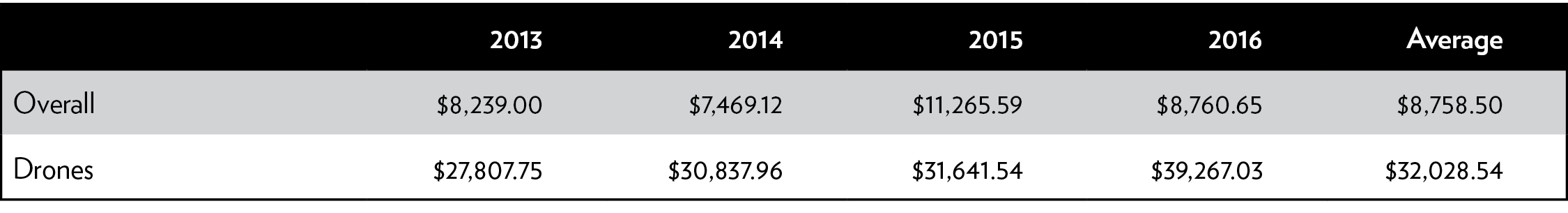
Each Predator B drone costs $17 million to purchase and $12,255 per flight hour to operate.22 Thus, CBP’s drone program cost a grand total of $255 million from 2013 to 2016 (Table 4).23 These figures likely understate the cost of the systems’ depreciation because they assume a 20-year lifespan, but 18 percent of CBP drones crashed in their first 10 years. For comparison, manned aircraft with surveillance capabilities similar to the Predator B cost only about $1,500 to $2,000 per flight hour.24 Each drone apprehension costs the federal government $32,000 (Table 5). This cost of drone apprehension compares with the average cost of apprehension of less than $9,000.25
Table 4: Flight hours and costs for Customs and Border Protection Predator B drones, 2013–2016
Sources: Department of Homeland Security Office of Inspector General; Government Accountability Office.
Table 5: Cost per apprehension by source of apprehension—Predator B drones and overall, 2013–2016
Sources: Author’s calculations based on Department of Homeland Security Office of Inspector General; Government Accountability Office; Customs and Border Protection.
In 2014, the Office of Inspector General for the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) found that CBP’s Predator B drone program’s effectiveness was unproven and did not meet program expectations.26 In 2016, DHS recommended that CBP not expand its drone program because of operational difficulties and exorbitant costs.27
Privacy Implications
No law requires CBP to obtain a warrant before using drones for surveillance, and the U.S. Supreme Court has upheld warrantless aerial surveillance in three cases.28 The CBP may establish its standards for surveillance and conduct operations without a court order or even suspicion that those under surveillance have committed a crime, thereby allowing the CBP to freely use its surveillance authority to collect information on the lives of law-abiding U.S. residents inside the United States. The quality of the drone footage and the long distances from the physical border where drones often operate considerably amplify this concern. Congress should establish clear and strict rules for CBP drone operations.
Drones allow for real-time, high-quality video feeds of the ground.29 Predator B drones are supposed to avoid urban areas, and CBP states that it does not deploy them to monitor protests and other activities protected by the First Amendment.30 Nonetheless, they collect enormous amounts of information on U.S. residents, including citizens, in border regions. CBP’s Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) drone authorization allows CBP drones to operate along and within 25 to 60 miles of the southern border and along and within 100 miles of the northern border.31 Residents are well aware of drone surveillance and may change their behavior in response.32
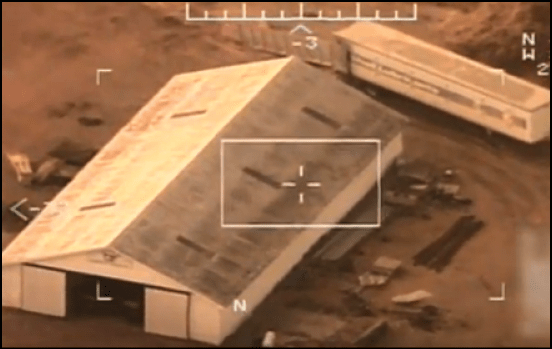
Each Predator B carries a ball camera that can stream live video in electrical optimal (Images 1 and 2) or infrared (Image 3).33 Some CBP drones also use Synthetic Aperture Radar, which allows for digital comparison of two areas of the border at different times to detect patterns in crossings.34 Two CBP drones in Arizona can carry VADER (Vehicle and Dismount Exploitation Radar), a brand of airborne tactical radar.35 VADER allows the drone to identify moving objects such as persons or vehicles and track them on the ground in real-time.
Image 1: CBP Predator electrical optimal
Source: U.S. Department of Homeland Security.
Image 2: Men with rifles in Iraq
Source: L’Espresso.
Image 3: Predator infrared image
Source: CNN.
The FAA requires Predator drones to fly between 19,000 to 28,000 feet.36 According to DHS, images from a Predator drone’s current camera cannot identify an individual’s exact height, weight, eye color, hairstyle, or facial image from such a high altitude, but they can identify backpacks, vehicle types, and firearms (Image 2).37 These limitations would not apply to the smaller drones that CBP is currently testing.38 Small drones fly closer to the ground and can identify people’s ethnicity, height, weight, and hairstyle. Image 4 is a frame from a video from one of CBP’s small drones.39 Small drones can identify faces, and operators are able to read license plates, signs, banners, and other writing from the air.
Image 4: CBP small drone image of the border
Source: U.S. Customs and Border Protection.
Worryingly, CBP wants to combine its small drones with facial recognition software that could compare drone-
captured images to a vast array of images in law enforcement databases.40 The FBI’s Facial Analysis, Comparison, and Evaluation (FACE) Services unit allows the agency to access driver’s license photos from 16 states and 411 million images from other sources, including the State and Defense departments.41 The FBI’s Next Generation Identification and the Interstate Photo System (NGI-IPS) include more than 30 million photos.42 Around half of all American adults are in a law enforcement facial recognition network.43
Facial recognition programs are prone to errors.44 A May 2016 Government Accountability Office report revealed that, although the FBI did not rigorously test the accuracy of NGI-IPS prior to deployment, what testing did take place found that the software failed 14 percent of the time to include the correct person in a 50-person list.45 Research on a number of facial recognition systems has found that their error rates are not evenly distributed among races and genders.46 If CBP’s small drones begin to use facial recognition technology, law enforcement agencies run the increased risk of detaining law-abiding people as suspected border crossers.
Non-Border Patrol Uses of Border Drones
CBP often uses its aircraft to assist non-Border Patrol operations.47 From 2010 to 2012, CBP operators flew 687 missions on behalf of other agencies.48 From 2013 to 2016, only about half of CBP drone flight hours were actually in support of Border Patrol.49 Furthermore, CBP reports that 20 percent of all Predator B flights were not in coastal or border areas.50 The cooperation between CBP and other federal agencies means that Americans living near the border aren’t the only ones who risk having their privacy infringed by CBP drones.
State and local agencies also often request CBP drone assistance for routine law enforcement matters. From 2013 to 2016, CBP drones flew 416 flight hours for state and local police, often failing to record which police departments were requesting CBP drone assistance.51 The first reported case of a drone aiding a domestic arrest occurred in 2011 when CBP deployed a drone without a warrant in North Dakota to determine whether suspects that local police were seeking to arrest were armed.52 A district judge rejected one of the suspect’s motion to suppress the warrantless drone surveillance, writing that “there was no improper use of an unmanned aerial vehicle.”53
DHS does not indicate whether CBP adheres to state warrant requirements when assisting local law enforcement agencies.54 For instance, Texas requires local police to obtain warrants to conduct searches with drones, whereas the other three southwest border states do not.55 Thus, CBP drones could be a loophole allowing local police to evade local democratic scrutiny of drone use or the requirement for a search warrant. Unfortunately, CBP fails to release sufficient data on local support operations to identify exactly how they are used.
Recommendations
If CBP chooses to continue flying expensive and ineffective drones, the agency should at least mandate the following privacy protections:
- CBP should use its drones solely for border security operations except in the case of states of emergency.
- CBP should not conduct drone surveillance more than five miles from the border.
- If CBP does use its drones to support state and local operations, it should ensure that its drone pilots comply with state and local drone legislation, including warrant requirements.
- CBP should not seek drones with facial recognition capability, which puts law-abiding Americans’ privacy at increased risk.
- At least six months before deploying new surveillance technology, CBP should disclose details about the technology’s capabilities, including information about the type of data to be collected, how long CBP plans to keep the data, when CBP will share the data, and with whom it will share the data.
- CBP should study replacing drones with surveillance technology that limits unnecessary data collection on U.S. residents.
Conclusion
CBP’s drone program has failed to live up to its expectations. Its expense, disproportionately small contribution to border security, and infringement on Americans’ privacy are good reasons for CBP to wind down its drone program. However, if CBP does continue to use drones, it should further constrain their use to prevent unnecessary data collection of Americans. China and other authoritarian countries have already begun to use drones to conduct domestic suspicionless surveillance, including of protesters and dissidents.56 The United States should put in place safeguards to prevent similar actions here.
Notes
1. Government Accountability Office, “Additional Actions Needed to Strengthen Collection of Unmanned Aerial Systems and Aerostats Data,” GAO-17-152, February 2017, http://www.gao.gov/assets/690/682842.pdf; and Alberto Cuadra and Craig Whitlock, “How Drones Are Controlled,” Washington Post, June 20, 2014, http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-srv/special/national/drone-crashes/how-drones-work/.
2. Office of Inspector General, “CBP’s Use of Unmanned Aircraft Systems in the Nation’s Border Security,” U.S. Department of Homeland Security, OIG-12-85, May 2012, https://www.oig.dhs.gov/assets/Mgmt/2012/OIG_12-85_May12.pdf.
3. “CBP to Test the Operational Use of Small Unmanned Aircraft Systems in 3 U.S. Border Patrol Sectors,” CBP Media Release, September 14, 2017, https://www.cbp.gov/newsroom/national-media-release/cbp-test-operational-use-small-unmanned-aircraft-systems-3-us-border; Avinc, “Puma™ AE RQ-20B,” 2017, https://www.avinc.com/images/uploads/product_docs/PumaAE_Datasheet_2017_Web_v1.1.pdf; and Avinc, “Raven® RQ-11A/B,” 2017, https://www.avinc.com/images/uploads/product_docs/Raven_Datasheet_2017_Web_v1.pdf.
4. FedBizOpps, “Small Unmanned Aircraft System (sUAS): Solicitation Number: HSHQDC-16-R-00114,” Department of Homeland Security, July 15, 2016, https://www.fbo.gov/index?s=opportunity&mode=form&id=5bb697a0dd83dccb4e011e905865f914&tab=core&_cview=0.
5. Mark Rockwell, “Border Agencies Test Hand-Launched Drones,” FCW, September 15, 2017, https://fcw.com/articles/2017/09/15/border-patrol-drone-tests.aspx.
6. This represents 5,540 combined flight hours/(365 days x 24 hours x 9 drones): Government Accountability Office, “Additional Actions Needed to Strengthen.”
7. Government Accountability Office, “Additional Actions Needed to Strengthen.”
8. Customs and Border Protection, “CBP Responds to Inspector General Report on Unmanned Aircraft Program,” September 28, 2016, https://www.cbp.gov/newsroom/video-gallery/video-library/cbp-responds-inspector-general-report-unmanned-aircraft-program.
9. Government Accountability Office, “Additional Actions Needed to Strengthen,” p. 28.
10. Government Accountability Office, “Additional Actions Needed to Strengthen Collection of Unmanned Aerial Systems and Aerostats Data” p. 49.
11. “Drones Patrol the Border for Illegal Immigrants,” CNN, May 12, 2010, https://youtu.be/yZHILC3vdKI?t=1m48s.
12. Shawn Musgrave, “The Mystery of US Customs’ Crashed Drone,” Motherboard, April 24, 2014, https://motherboard.vice.com/en_us/article/jp5pg4/the-mystery-of-us-customs-crashed-drone; and Arthur Rotstein, “Operator Fired in ’06 Crash of Unmanned Aerial Drone,” Associated Press, October 18, 2007, http://tucson.com/news/local/border/operator-fired-in-crash-of-unmanned-aerial-drone/article_b4cd0e8a-596d-5c5a-bea1-3b7ab1188325.html.
13. Emily Chow, Alberto Cuadra, and Craig Whitlock, “Fallen from the Skies,” Washington Post, June 20, 2014, http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-srv/special/national/drone-crashes/database/; “2016 USAF Almanac,” Air Force Magazine 99, no. 5 (May 2016), http://secure.afa.org/joinafa/AFMag0516/files/downloads/attachments/0516fullissue.pdf; and Craig Whitlock, “When Drones Fall from the Sky,” Washington Post, June 20, 2014, http://www.washingtonpost.com/sf/investigative/2014/06/20/when-drones-fall-from-the-sky/?utm_term=.c96f4eb5079b.
14. Whitlock, “When Drones Fall from the Sky.”
15. Government Accountability Office, “Additional Actions Needed to Strengthen,” p. 49.
16. Office of Inspector General, “U.S. Customs and Border Protection’s Unmanned Aircraft System Program Does Not Achieve Intended Results or Recognize All Costs of Operations,” Department of Homeland Security, OIG-15-17, December 24, 2014, https://www.oig.dhs.gov/assets/Mgmt/2015/OIG_15-17_Dec14.pdf.
17. Government Accountability Office, “Additional Actions Needed to Strengthen”; and United States Border Patrol, “Total Illegal Alien Apprehensions by Fiscal Year,” https://www.cbp.gov/sites/default/files/assets/documents/2017-Dec/BP%20Total%20Apps%2C%20Mexico%2C%20OTM%20FY2000-FY2017.pdf.
18. Government Accountability Office, “Additional Actions Needed to Strengthen”; and Customs and Border Protection, “CBP Enforcement Statistics FY2018,” https://www.cbp.gov/newsroom/stats/cbp-enforcement-statistics.
19. Associated Press, “Half of US-Mexico Border Now Patrolled Only by Drone,” Guardian, November 13, 2014, https://www.theguardian.com/world/2014/nov/13/half-us-mexico-border-patrolled-drone.
20. Government Accountability Office, “Additional Actions Needed to Strengthen.”
21. For 2014 and 2015, CBP reported that an average of 190,000 per year made it across the border. Tribune News Services, “Barely Half of Illegal Border Crossers Caught, According to Homeland Security Report,” Chicago Tribune, October 7, 2016, http://www.chicagotribune.com/news/nationworld/ct-us-mexico-border-crossing-captures-20161006-story.html.
22. Office of Inspector General, “U.S. Customs and Border Protection’s Unmanned Aircraft System Program Does Not Achieve.”
23. Office of Inspector General, “U.S. Customs and Border Protection’s Unmanned Aircraft System Program Does Not Achieve.”
24. Bob Ortega, “Is Pricey Border Patrol Drone Program Worth the Cost?” Arizona Republic, July 21, 2015, https://www.azcentral.com/story/news/arizona/investigations/2015/06/21/border-patrol-drone-program/28999735/v.
25. Obtained by dividing the entire Border Patrol budget by number of apprehensions: United States Border Patrol, “Enacted Border Patrol Program Budget by Fiscal Year (Dollars in Thousands),” 2017, https://www.cbp.gov/sites/default/files/assets/documents/2017-Dec/BP%20Budget%20History%201990-2017.pdf.
26. Office of Inspector General, “U.S. Customs and Border Protection’s Unmanned Aircraft System Program,” p. 1.
27. Government Accountability Office, “Additional Actions Needed to Strengthen.”
28. Dow Chemical Co. v. United States, 476 U.S. 227 (1986); California v. Ciraolo, 476 U.S. 207 (1986); and Florida v. Riley, 488 U.S. 445 (1989).
29. Department of Homeland Security, “Privacy Impact Assessment for the Aircraft Systems,” DHS/CBP/PIA-018, September 9, 2013, https://www.dhs.gov/sites/default/files/publications/privacy-pia-cbp-aircraft-systems-20130926.pdf.
30. Department of Homeland Security, “Best Practices for Protecting Privacy, Civil Rights & Civil Liberties in Unmanned Aircraft Systems Programs,” U.S. Department of Homeland Security Privacy, Civil Rights & Civil Liberties Unmanned Aircraft Systems Working Group, December 18, 2015, https://www.dhs.gov/sites/default/files/publications/UAS%20Best%20Practices.pdf.
31. Department of Homeland Security, “Privacy Impact Assessment for the Aircraft Systems”; and United States v. Ramsey, 431 U.S. 606 (1977).
32. Todd Miller, “War on the Border,” New York Times, August 17, 2013, http://www.nytimes.com/2013/08/18/opinion/sunday/war-on-the-border.html.
33. Department of Homeland Security, “Privacy Impact Assessment for the Aircraft Systems.”
34. Office of Inspector General, “U.S. Customs and Border Protection’s Unmanned Aircraft System Program.”
35. Office of Inspector General, “U.S. Customs and Border Protection’s Unmanned Aircraft System Program”; Robert Beckhusen, “Army Works to Ensure Homemade Bombs Don’t Escape the Gaze of ‘Vader,’” Wired, December 7, 2012, https://www.wired.com/2012/12/vader/; and Brian Bennett, “Radar Shows U.S. Border Security Gaps,” Los Angeles Times, April 3, 2013, http://articles.latimes.com/2013/apr/03/nation/la-na-border-radar-20130404.
36. Department of Homeland Security, “Privacy Impact Assessment for the Aircraft Systems.”
37. U.S. Customs and Border Protection, “Unmanned Aircraft System MQ-9 Predator B,” https://www.cbp.gov/sites/default/files/documents/FS_2015_UAS_FINAL_0.pdf; and Gianluca Di Feo, “Così i droni italiani spiano i covi del Califfo,” L’Espresso, December 10, 2015, http://espresso.repubblica.it/plus/articoli/2015/12/10/news/esclusivo-espresso-cosi-droni-italiani-spiano-il-califfo-1.242989?refresh_ce.
38. Rockwell, “Border Agencies Test Hand-Launched Drones.”
39. “Drone Footage Shows Prototype Border Walls at U.S.-Mexico Border,” Washington Post, October 19, 2017, https://www.washingtonpost.com/video/national/drone-footage-shows-prototype-border-walls-at-us-mexico-border/2017/10/19/3d79c380-b4b7-11e7-9b93-b97043e57a22_video.html?utm_term=.05e9ff255689.
40. Matthew Feeney, “Border Patrol Seeking Facial Recognition Drones,” Cato at Liberty, April 10, 2017, https://www.cato.org/blog/border-patrol-seeking-facial-recognition-drones.
41. Government Accountability Office, “FBI Should Better Ensure Privacy and Accuracy,” GAO-16-267, May 2016, http://www.gao.gov/assets/680/677098.pdf.
42. Government Accountability Office, “FBI Should Better Ensure Privacy and Accuracy.”
43. Government Accountability Office, “FBI Should Better Ensure Privacy and Accuracy”; and Clare Garvie, Alvaro Bedoya, and Jonathan Frankle, “The Perpetual Line-Up,” Georgetown Law Center on Privacy and Technology, October 18, 2016, https://www.perpetuallineup.org.
44. Government Accountability Office, “FBI Should Better Ensure Privacy and Accuracy.”
45. Government Accountability Office, “FBI Should Better Ensure Privacy and Accuracy.”
46. Clare Garvie and Jonathan Frankle, “Facial-Recognition Software Might Have a Racial Bias Problem,” The Atlantic, April 7, 2016, https://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2016/04/the-underlying-bias-of-facial-recognition-systems/476991/; Steve Lohr, “Facial Recognition Is Accurate, if You’re a White Guy,” New York Times, February 9, 2018, https://www.nytimes.com/2018/02/09/technology/facial-recognition-race-artificial-intelligence.html; and Brendan Klare et al., “Face Recognition Performance: Role of Demographic Information,” IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 7, no. 6 (December 2012): 1789–1801, https://assets.documentcloud.org/documents/2850196/Face-Recognition-Performance-Role-of-Demographic.pdf.
47. Department of Homeland Security, “Privacy Impact Assessment for the Aircraft Systems.”
48. Craig Whitlock and Craig Timberg, “Border-Patrol Drones Being Borrowed by Other Agencies More Often than Previously Known,” Washington Post, January 14, 2014, https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/national-security/border-patrol-drones-being-borrowed-by-other-agencies-more-often-than-previously-known/2014/01/14/5f987af0-7d49-11e3-9556-4a4bf7bcbd84_story.html?utm_term=.113befbca5f4.
49. Government Accountability Office, “Additional Actions Needed to Strengthen.”
50. Government Accountability Office, “Additional Actions Needed to Strengthen,” p. 9.
51. “2 percent of Predator B flight hours from fiscal years 2013 through 2016 were attributed to support for state and local government agencies.” Two percent of 20,780 hours is 415.6 hours. See Government Accountability Office, “Additional Actions Needed to Strengthen,” p. 15.
52. Michael Peck, “Predator Drone Sends North Dakota Man to Jail,” Forbes, January 27, 2014, https://www.forbes.com/sites/michaelpeck/2014/01/27/predator-drone-sends-north-dakota-man-to-jail/#715b52bd324c; Brian Bennett, “Police Employ Predator Drone Spy Planes on Home Front,” Los Angeles Times, December 10, 2011, http://articles.latimes.com/2011/dec/10/nation/la-na-drone-arrest-20111211.
53. Jason Koebler, “North Dakota Man Sentenced to Jail in Controversial Drone-Arrest Case,” U.S. News and World Report, January 15, 2014, https://www.usnews.com/news/articles/2014/01/15/north-dakota-man-sentenced-to-jail-in-controversial-drone-arrest-case.
54. Department of Homeland Security, “Privacy Impact Assessment for the Aircraft Systems,” DHS/CBP/PIA-018, September 9, 2013, https://www.dhs.gov/sites/default/files/publications/privacy-pia-cbp-aircraft-systems-20130926.pdf; Department of Homeland Security, “Best Practices.”
55. Texas’s drone warrant requirement is subject to exceptions. For instance, Texas law enforcement can forgo a warrant if they are “in immediate pursuit of a person law enforcement officers have reasonable suspicion or probable cause to suspect has committed an offense, not including misdemeanors or offenses punishable by a fine only.” Texas Gov. Code Ann. § 423.002 (2013). In 2015, the New Mexico Supreme Court did rule that warrantless helicopter surveillance that caused disruption to the property being surveilled did violate the Fourth Amendment. State v. Davis, 2015–S–1–SC–34548: “prolonged hovering close enough to the ground to cause interference with Davis’ property transformed this surveillance from a lawful observation of an area left open to public view to an unconstitutional intrusion into Davis’ expectation of privacy.” Allie Bohm, “Status of 2014 Domestic Drone Legislation in the States,” ACLU, April 22, 2014, https://www.aclu.org/blog/status-2014-domestic-drone-legislation-states.
56. Didi Kirsten Tatlow, “China Said to Deploy Drones after Unrest in Xinjiang,” New York Times, August 19, 2014, https://sinosphere.blogs.nytimes.com/2014/08/19/china-said-to-deploy-drones-after-unrest-in-xinjiang/?_php=true&_type=blogs&_r=0.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.