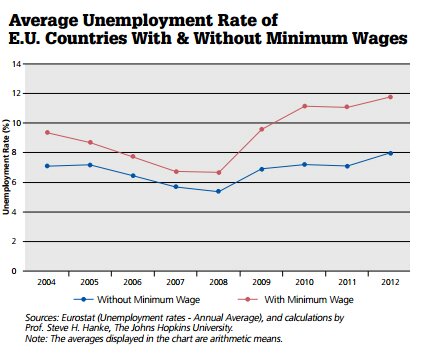
President Obama set the chattering classes abuzz after his recent unilateral announcement to raise the minimum wage for newly hired Federal contract workers. During his State of the Union address in January, he sang the praises for his decision, saying that “It’s good for the economy; it’s good for America.” As the worldwide economic slump drags on, the political drumbeat to either introduce minimum wage laws (read: Germany) or increase the minimums in countries where these laws exist — such as Indonesia — is becoming deafening. Yet the glowing claims about minimum wage laws don’t pass the most basic economic tests. Just look at the data from Europe (see the accompanying chart).
There are seven European Union (E.U.) countries in which no minimum wage is mandated (Austria, Cyprus, Denmark, Finland, Germany, Italy, and Sweden). If we compare the levels of unemployment in these countries with E.U. countries that impose a minimum wage, the results are clear. A minimum wage leads to higher levels of unemployment. In the 21 countries with a minimum wage, the average country has an unemployment rate of 11.8%. Whereas, the average unemployment rate in the seven countries without mandated minimum wages is about one third lower — at 7.9%.
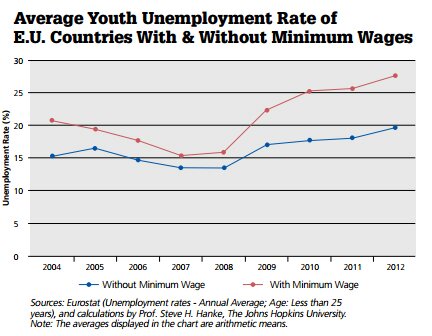
This point is even more pronounced when we look at rates of unemployment among the E.U.'s youth — defined as those younger than 25 years of age (see the accompanying chart).
In the twenty-one E.U. countries where there are minimum wage laws, 27.7% of the youth demographic — more than one in four young adults — was unemployed in 2012. This is considerably higher than the youth unemployment rate in the seven E.U. countries without minimum wage laws — 19.5% in 2012 — a gap that has only widened since the Lehman Brothers collapse in 2008.
So, minimum wage laws — while advertised under the banner of social justice — do not live up to the claims made by those who tout them. They do not lift low wage earners to a so-called "social minimum". Indeed, minimum wage laws — imposed at the levels employed in Europe — push a considerable number of people into unemployment. And, unless those newly unemployed qualify for government assistance (read: welfare), they will sink below, or further below, the social minimum.
As Nobelist Milton Friedman correctly quipped, "A minimum wage law is, in reality, a law that makes it illegal for an employer to hire a person with limited skills."
Dr. Jens Weidmann, President of Germany's Bundesbank,must have heard Prof. Friedman and looked at these European data before he took on Chancellor Angela Merkel for proposing the introduction of a minimum wage law in Germany. In short, Dr. Weidmann said that this would damage Germany's labor market and be a German job killer. He is right.
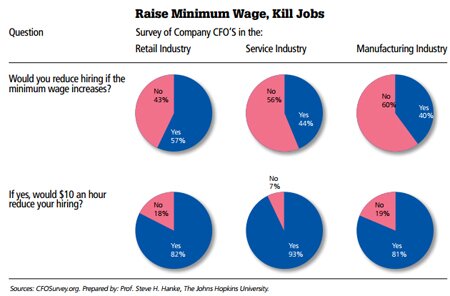
And, executives surveyed in the recently released Duke University/CFO Magazine Global Business Outlook Survey agree, too. Indeed, Chief Financial Officers from around the world were interviewed and a significant number of them concurred: a minimum wage increase in the United States –from the current $7.25/hour to President Obama's proposed $10.10/hour — would kill U.S. jobs. The accompanying table shows what the CFOs had to say.
Perhaps, Prof. Friedman said it best when he concluded that "The real tragedy of minimum wage laws is that they are supported by well-meaning groups who want to reduce poverty. But the people who are hurt most by high minimums are the most poverty stricken."
High mandated minimum wages will throw people out of work and onto the welfare rolls in cases where unemployment benefits exist. When it comes to welfare payments, they obey the laws of economics, too. Indeed, if something — like unemployment — is subsidized, more of it will be produced. When the data on unemployment benefits speak, they tell us that if the unemployed receive unemployment benefits, the chances that they will become employed are reduced. Those data also show that the probability of an unemployed worker finding employment increases dramatically the closer an unemployed worker comes to the termination date for receipt of his unemployment benefits. In short, when the prospect of losing welfare benefits raises its head, unemployed workers magically tend to find work.
The most important lesson to take away from allowing the minimum wage and unemployment benefit data to talk is that abstract notions of what is right, good and just should be examined from a concrete, operational point of view. A dose of reality is most edifying.